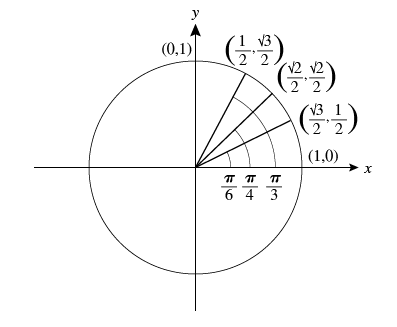
1 Radians to Quadrants = 70 Radians to Quadrants = 2 Radians to Quadrants = 80 Radians to Quadrants = 3 Radians to Quadrants = 90 Radians to Quadrants = 4 Radians to Quadrants = 100 Radians to Quadrants = 5 Radians to Quadrants = 311 0 Radians to Quadrants =Solution The angle 5ˇ 4 will fall in quadrant 2 with a reference angle of r = ˇ 4 Using either a special right triangle or the unit circle, we nd that csc 5ˇ 4 = csc ˇ 4 = 1 sin ˇ 4 = 1 p1 2 = p 2 (e) sec 48ˇ 3 Solution The angle 48ˇ 3 = 16ˇis a quadrantal angle that is coterminal to 2ˇ Thus, sec 48ˇ 3 = sec(16ˇ) = 1 cos16ˇ = 1 cos2ˇ = 1 1 = 1 (f) cos 11ˇ 3 Solution TheIf the terminal arm of an angle falls in quadrants 2, 3 or 4, we use a reference angle of 6;
Section 4 3 Precalculus Final
How to find angle in 3rd quadrant
How to find angle in 3rd quadrant-The symmetry of the diagram gives θ 2 = −1313 π = 18 radians;Buy Quadrant mouldings at B&Q Click & Collect available 135 day returns 1000s of DIY supplies free delivery on orders over £50
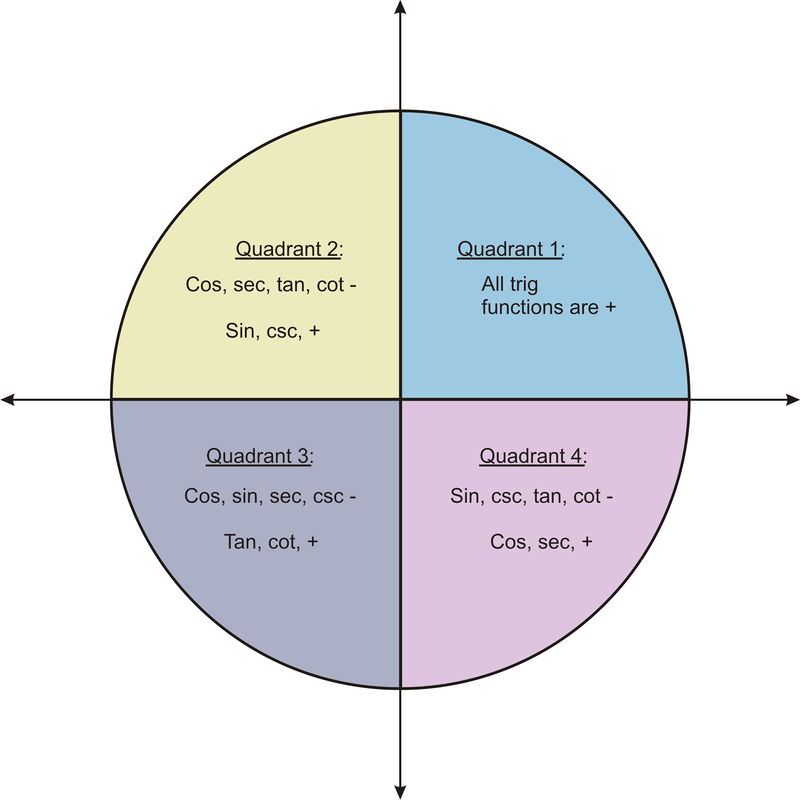


Domain Range And Signs Of Trigonometric Functions Read Trigonometry Ck 12 Foundation
Show per page Sort By Set Descending Direction Freefoam 28mm Square Edge Window Batten Plastic Trim 25 Metre (FB28) £125 £150 Add to Basket Add to Compare2 If t is a firstquadrant angle in standard position with P(u, v) = (3, 4), evaluate tan t Tan(t) = y/x = 4/3 ===== Cheers, Stan H Answer by Alan3354() (Show Source) You can put this solution on YOUR website!\x = {\cos ^{ 1}}\left( {\frac{1}{2}} \right)\ Solve in the same way as you would have had it been in degrees As with equations in degrees, decide on the appropriate quadrants and then apply
2 For angles in quadrants 24, determine the related acute angle β Using a calculator, determine what the value of the desired ratio would be for angle β 3 The desired ratio for angle θ will be the value obtained from step 2, but with its sign adjusted as follows • if θ is in quadrant 2, only the sine ratio is positive;The 4 Graph Quadrants There are four graph quadrants that make up the Cartesian plane Each graph quadrant has a distinct combination of positive and negative values Here are the graph quadrants and their values Quadrant I The first quadrant is in the upper righthand corner of the plane Both x and y have positive values in this quadrant Quadrant II The second quadrant isAll others are negative • if θ is in quadrant 3, only the
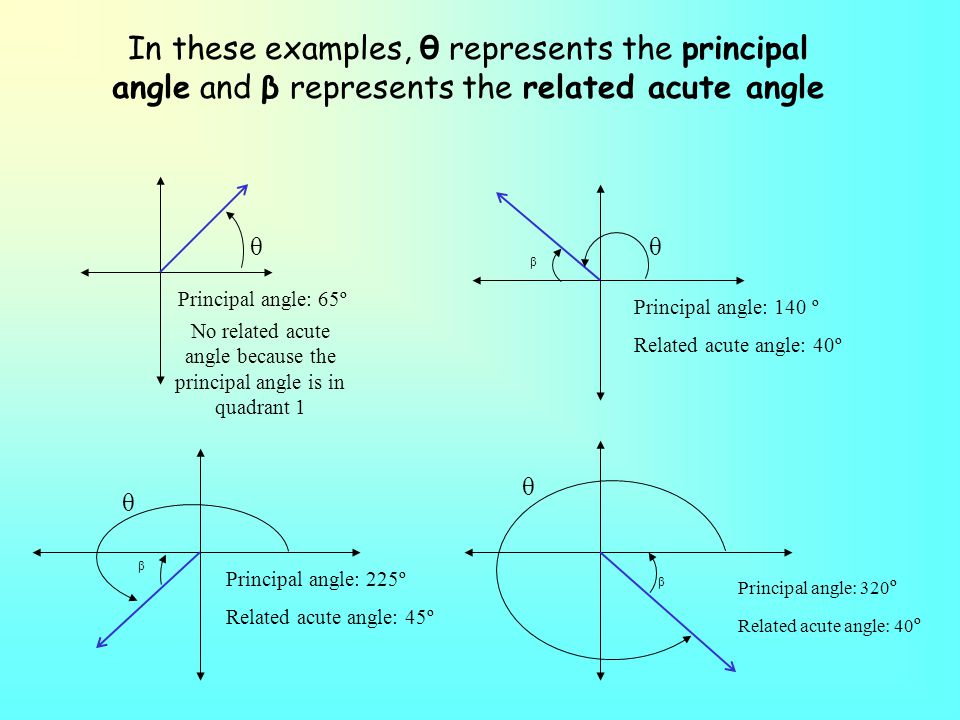
CAST still goes counterclockwise but starts in quadrant 4 going through quadrants 4, 1, 2, then 3 ACTS still starts in quadrant 1 but goes clockwise going through quadrants 1, 4, 3, then 2 Sines and cosines of special angles Sines and cosines of common angles 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90° follow the pattern with n = 0, 1, , 4 for sineI don't really understand the doubleangle or the halfangle formula Here are some problems I need to do 1 If cos x = and x is a fourthquadrant angle, evaluate sin 2xNo26/11/15 · Johnson Z Nov 26, 15 The related acute is an acute angle (< 90∘) that can be found between the terminal arm and the xaxis when the terminal arm is in quadrants 2, 3, or 4 There is no related acute angle if the terminal arm lies in quadrant 1


Signs Of Sin Cos Tan In Different Quadrants Finding Value Of Trign



The Unit Circle Ck 12 Foundation
Defining Sine and Cosine Functions Now that we have our unit circle labeled, we can learn how the \((x,y)\) coordinates relate to the arc length and angleThe sine function relates a real number \(t\) to the ycoordinate of the point where the corresponding angle intercepts the unit circleMore precisely, the sine of an angle \(t\) equals the yvalue of the endpoint on the unit circle of anThe product is (–2) × (–1) = 2, which is positive Any other product in Quadrant III will be positive also, so Quadrant III is not part of my answer In Quadrant IV, I'll pick, say, (3, –4) The product is 3 × (–4) = –12, which is negative Any other product in Quadrant IV will be negative also, so Quadrant IV is part of my answer(1) I (3) III (2) II (4) IV
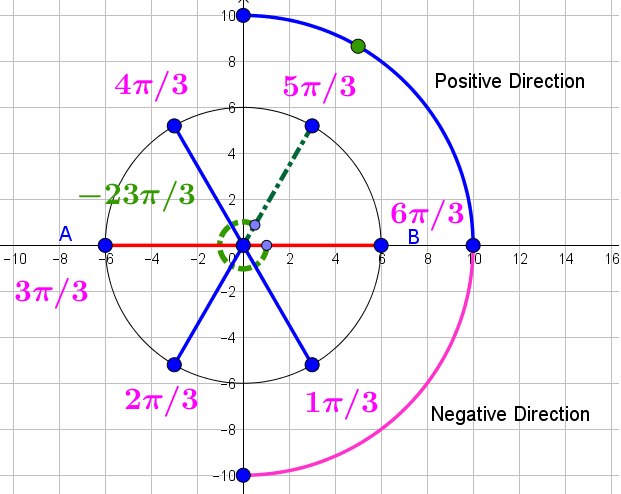


How Do You Sketch The Angle In Standard Position 23pi 3 Socratic
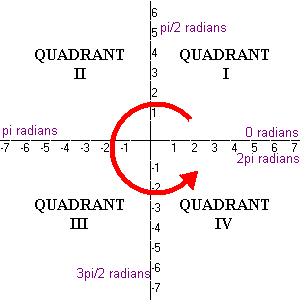


How Do You Determine The Quadrant In Which 6 02 Radians Lies Socratic
Namaste to all Friends, This Video Lecture Series presented By VEDAM Institute of Mathematics is Useful to all studentThe values of sin, cos, tan, cot at the angles of 0°, 30°, 60°, 90°, 1°, 135°, 150°, 180°, 210°, 225°, 240°, 270°, 300°, 315°, 330°, 360°Then you either need to get a properly measured clockwise angle between 0 and 2PI to send to your method or you need to work out if it is in quadrants 1/2 or 3/4 first and then you can use an angle such as you have (ie the smaller angle at the meeting point) and work out one or two and then if appropriate map that to four/three (wubtracting from five should do that last bit)


Coordinate Geometry Gmat Math Study Guide



Trigonometric Circle Used To Convert The Angles From Quadrants 2 3 And Download Scientific Diagram
Formulas for finding reference angles and a set of examplesRadians lies in Quadrant 1) I 2) II 3) III 4) IV 8 An angle that measures 5π 6 radians is drawn in standard position In which quadrant does the terminal side of the angle lie?UPVC Window Batten & Quadrant Trim;
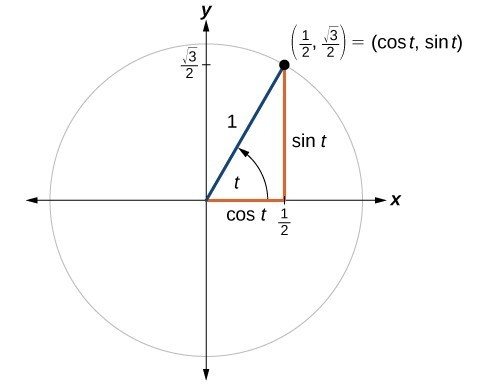


Unit Circle Sine And Cosine Functions Precalculus Ii
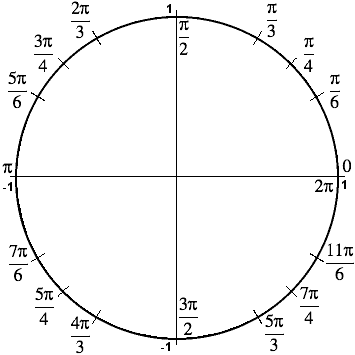


Trigonometry Facts The Amazing Unit Circle
Freefoam Plastic Quadrant Window Trim (125 metre x 4) White, 19mm (FQ19) Excl VAT £299 Incl VAT £3594 and 3 in conjunction with the CAST rule to determine the value and the sign J GarvinExact Values of Trigonometric Ratios Slide 6/16 Using the 12p 3 triangle, the opposite side to 3 has a length of p 3, while the hypotenuse has a length of 2 Therefore, sin 3 = p 3 2 J GarvinExact Values ofThirdangle projection is most commonly used in America, Japan (in JIS B 0001:10);
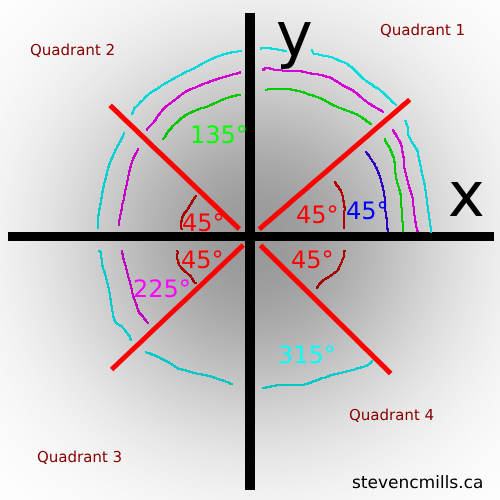


01 19 19 One Lesson Of Math Angles In Standard Position In All Quadrants Part 1



Domain Range And Signs Of Trigonometric Functions Read Trigonometry Ck 12 Foundation
Because we want answers between 0 and 2π we 'correct' θ PV by adding 2π (to get 4Section 43 Exercises 1 The 450° angle lies on the positive–y axis (450°360°=90°), while the others are all coterminal in Quadrant II 2 The angle lies in Quadrant I , while the others are all coterminal in Quadrant IV In #3–12, recall that the distance from the origin is r= 3 sin ¨= , cos ¨=– , tan ¨=–2;2 days ago · Your first angle in quadrant 2 will be 2π/3 Adding together the 2 in the numerator and the 3 in the denominator will yield 5 Look at the angle straight across in quadrant 4 (bottom right quarter of the circle) Place this 5 in the numerator in front of π Repeat this process for the other two angles in quadrants 2 and 4 We'll repeat the same process for quadrants 1 (top right) and 3



Rectangular Coordinate System


The Trigonometry Functions
(1) 1 (3) 210 (2) 60 (4) 240 3 A rotation angle, drawn in standard position, measures 10 In which quadrant does its terminal ray lie?Plastic Trims, Angles, Quadrants & Architraves Items 136 of 134 Page You're currently reading page 1;A) cos 121˚ is in quadrant II (90˚ < 121˚ < 180˚) In quadrant II, only sine is positive, so cos121˚ is negative b) tan 2˚ is in quadrant III (180˚ < 2˚ < 270˚) In quadrant III, tangent is positive, so tan 2˚ is positive Unit Circle, Reference Angle and Signs of Trig Functions in 4 Quadrants Show Stepbystep Solutions
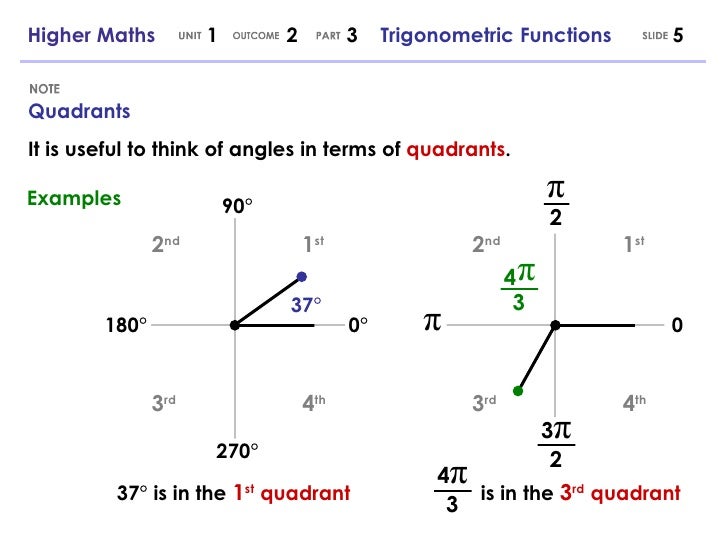


Higher Maths 1 2 3 Trigonometric Functions


Unit Circle Trigonometry
Example Find the two angles θ between 0 and 2π radians for which tan(θ) = −38 The CAST diagram for negative tangent is as shown The calculator or Algebra Coach gives θ PV = arctan(−38) = −1313 radians;Sal first finds the direction angle of a vector in the first quadrant, then moves onto a trickier one in the second quadrant Sal first finds the direction angle of a vector in the first quadrant, then moves onto a trickier one in the second quadrant If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website If you're behind a web filter, please2 If drawn in the standard position, which of the following angles terminates in the third quadrant?
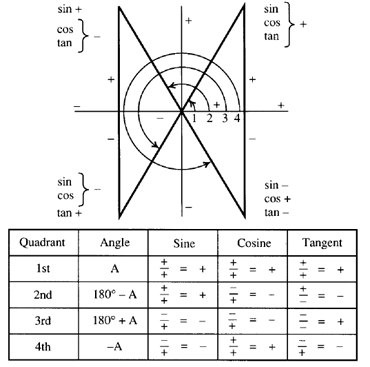


Trigonometric And Geometric Conversions Sin A B Sin A B Sin Ab



Coordinate Worksheets
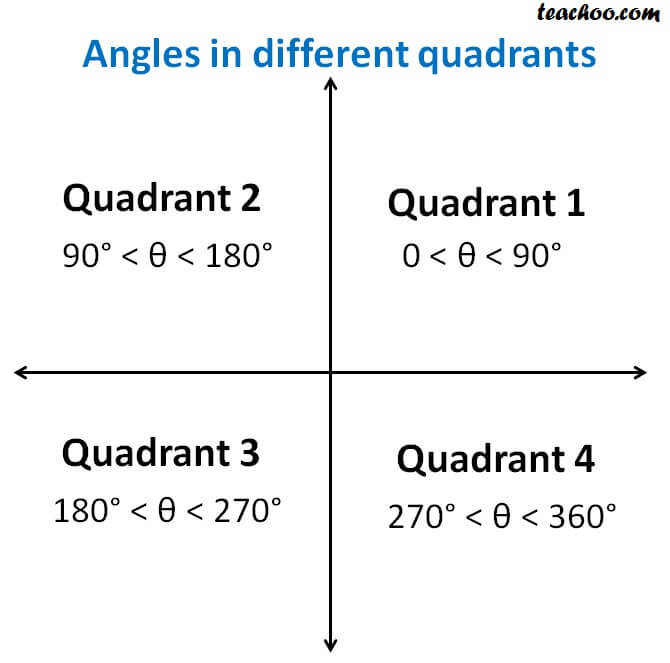
29/05/18 · Transcript Let s see the angles in different Quadrants In Quadrant 1, angles are from 0 to 90 In Quadrant 2, angles are from 90 to 180 In Quadrant 3, angles are from 180 to 270 In Quadrant 4, angles are from 270 to 360 To learn sign of sin, cos, tan in different quadrants, we remember Add Sugar To Coffee Representing as a table Quadrant I Quadrant II Quadrant III QuadrantGet trade quality quadrant beading priced low Quality assured since 1972 Visit one of 230 stores or buy online!All graphs have an x and y axis Coordinates, written as an ordered pair of numbers, are used to give positions on a graph The xaxis is horizontal (across), while the yaxis is vertical (updown)


Section 4 3 Precalculus Final
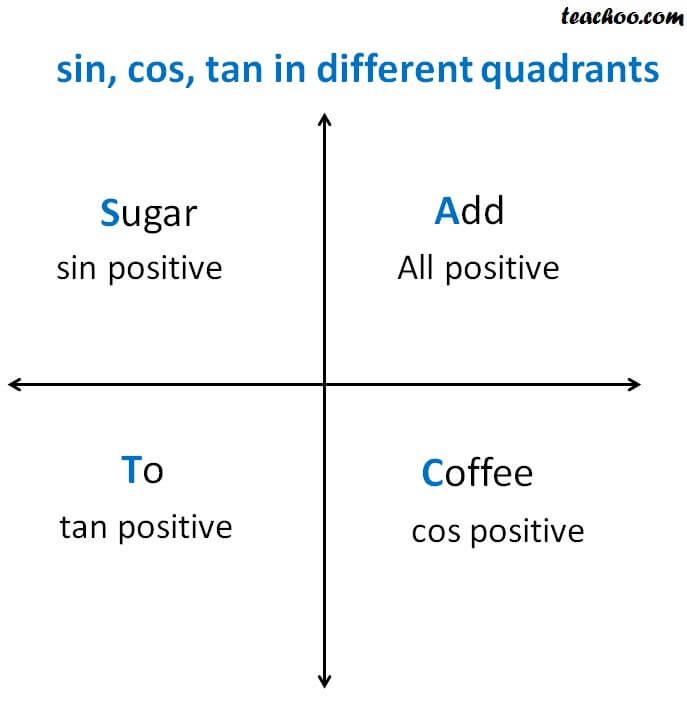


Signs Of Sin Cos Tan In Different Quadrants Finding Value Of Trign
10 An angle with measure 7π 4 radians is in standard position In which quadrantPlastic Trims, Angles, Quadrants & Architraves ;2 Degrees to Quadrants = 80 Degrees to Quadrants = 0 3 Degrees to Quadrants = 90 Degrees to Quadrants = 1 4 Degrees to Quadrants = 100 Degrees to Quadrants = 5 Degrees to Quadrants = 0 Degrees to Quadrants = 6 Degrees to Quadrants = 300 Degrees to Quadrants = 7 Degrees to
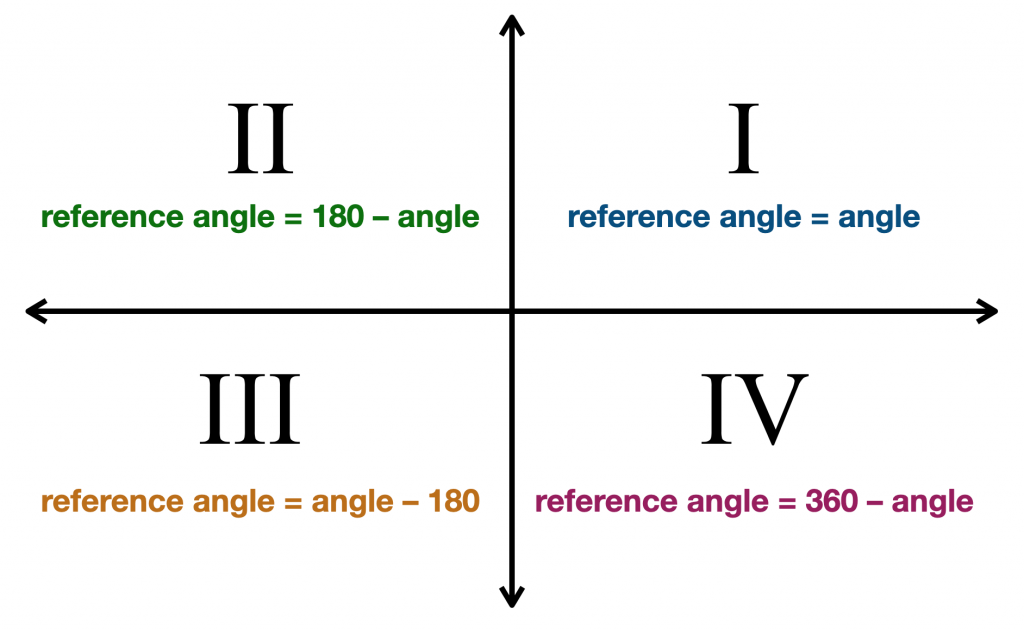


Reference Angle Calculator Pi Day
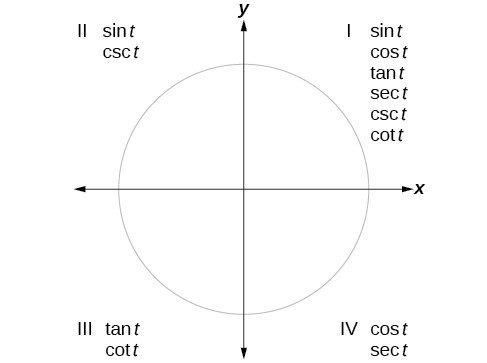


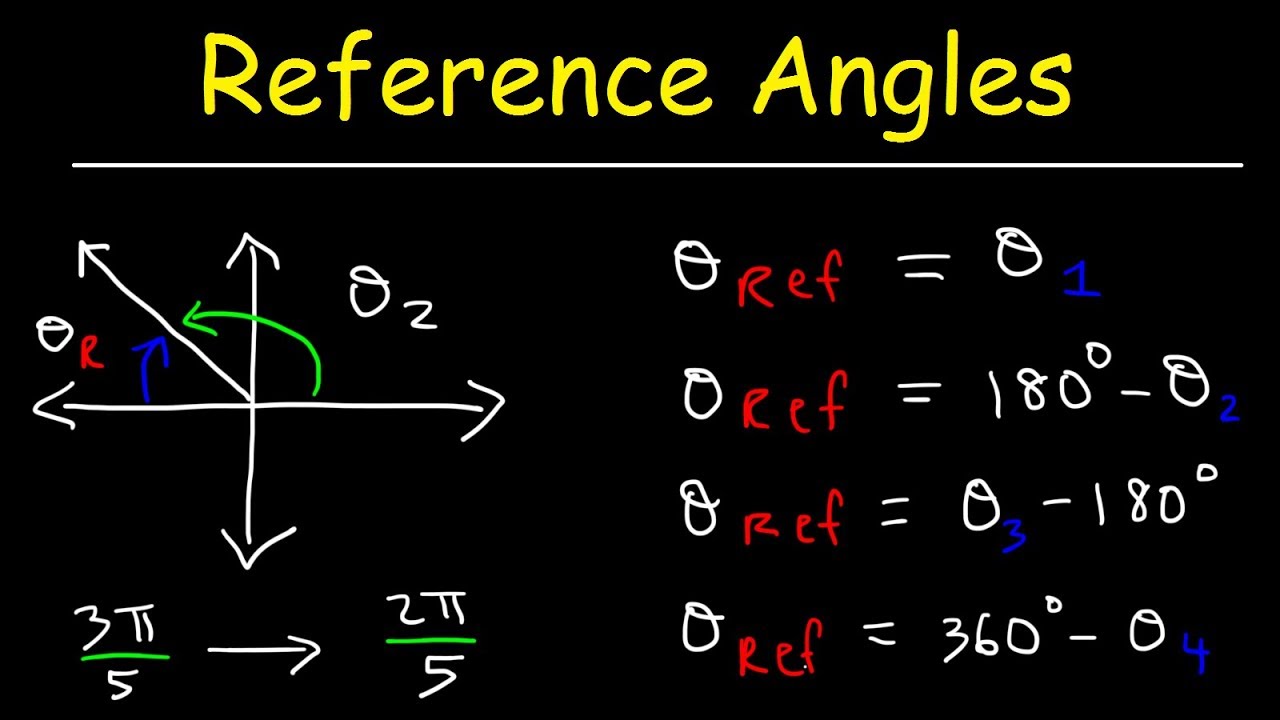
Section 4 4 Reference Angles Precalculus
/03/17 · The angle θ lies in Quadrant II cosθ=−2/3 What is tanθ ?22/04/21 · Since, 1 cycle is 2π radians, so it is a bit less than two cycles but more than 3/2 = 15 This angle thus lies in the fourth quadrant between 3π/2 and 2π radians Now, as we know, for fourth quadrant Reference Angle = 2 π – Given Angle, here given angle = 16/9 π radians = 2 π – 16/9 π = 2/9 π Hence the reference angle to 16/9 π radians is 2/9 π Last modified on April 22nd,The basic geometry rule for finding the quadrant of the coordinate points are 1) If both coordinates are positive, then the point lies in first quadrant 2) If x is negative and y is positive, then the point lies in second quadrant 3) If both coordinates are negative, then the point lies in third quadrant 4) If is x is positive and y is


Solved The Unit Circle In Detail In Figure 4 There Ar Chegg Com



Content The Four Quadrants
Update The angle θ lies in Quadrant IV sinθ=−2/3 What is cosθ ?UPVC Window Batten & Quadrant Trim Items 136 of 47 Page You're currently reading page 1;Show per page Sort By Set Descending Direction Mr Plastic 25mm x 25mm Plastic Angle 25 Metre White () £327 £392 Add to Basket Add to Compare Mr Plastic 25mm x 25mm Plastic Angle 5 Metre White () £640 £768


Solved Identify The Quadrant Or Quadrants For The Angles Chegg Com



Unit Circle Memorizing The First Quadrant Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
9 An angle that measures 5π 3 radians is drawn in standard position In which quadrant does the terminal side of the angle lie?The given angle may be in degrees or radians Use of calculator to Find the Quadrant of an Angle 1 Enter the angle in Degrees top input example 1250 in Radians second input as a fraction of π Example 27/5 π or 12 π then press the button "Find Quadrant" on the same row If you enter a quadrantal angle, the axis is displayed ExampleNote that in each case, all that really mattered was the sixtydegree triangle in the quadrant where the angle terminated, and the x and yvalues in that quadrantThe fact that you can't draw a right triangle with a base angle of 300° was irrelevant To find the trig ratios, you needed only to draw the terminal side of the angle in whatever quadrant it happened to land, construct a right


How To Find The Reference Angle In Radians And Degrees Trigonometry Youtube
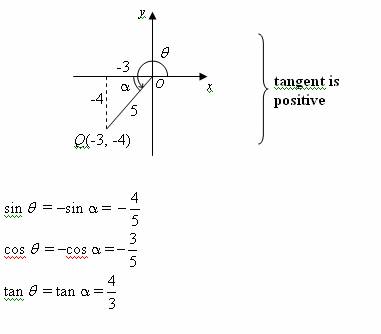


Trigonometric Ratios Solutions Examples Videos
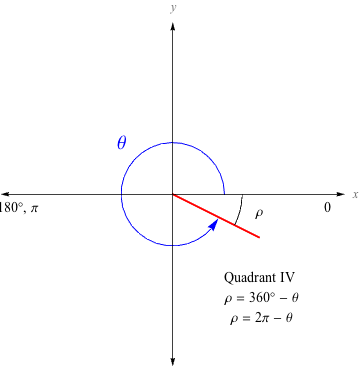
18/12/10 · 2) 60 degrees This is the same as 60 360 = 300 degrees, which is Quadrant IV 3) 480 degrees This is the same as 480 360 = 1 degrees, which is Quadrant II 4) 270 degrees This is the angle that divides Quadrant III from Quadrant IV 5) tan x > 0 This is true when sine and cosine are both positive or both negative, which makes itThe quadrants are named in increasing order, starting with quadrant 1 (QI) in the top right, and moving counterclockwise to QII in the top left, etc In this way, higher numbered quadrants contain bigger angles (until 360°, of course) So the angle −34° lies in QIVAnd is preferred in Australia, as laid down in AS —1992 633 In the UK, BS 9721 allows for three different conventions for arranging views Labelled Views, Third Angle Projection, and First Angle Projection See also


In Which Quadrant Does 90 Degrees Lie Quora
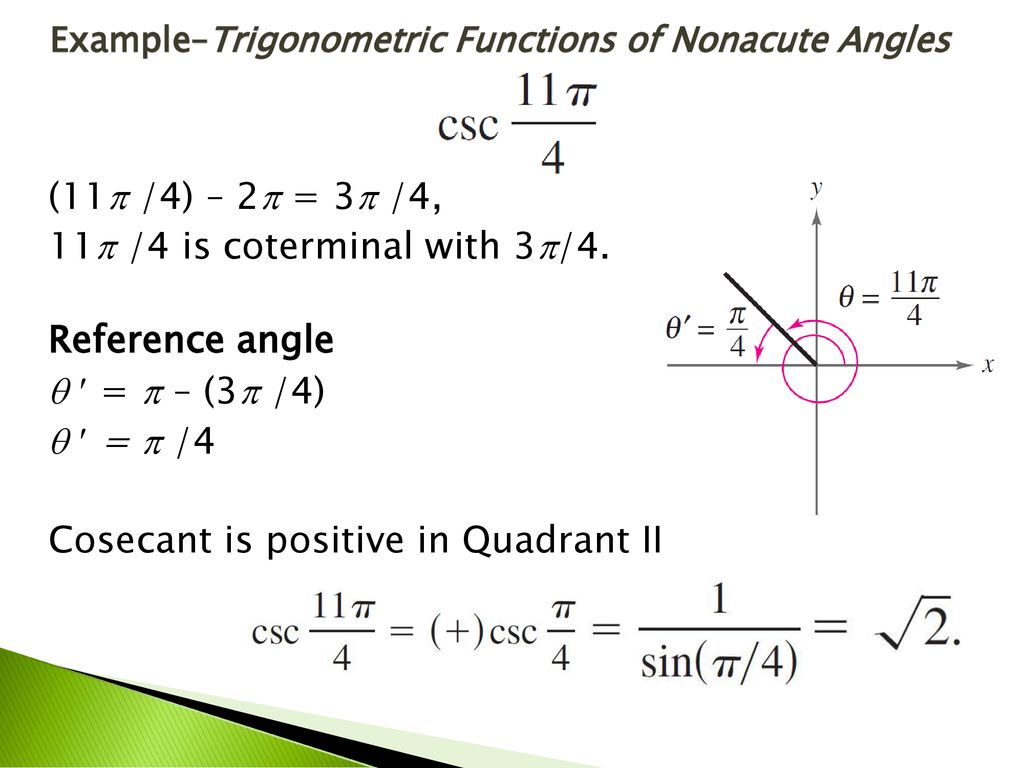


Trigonometric Functions Of Any Angle Ppt Download
Answer Save 2 Answers Relevance Mathmom Lv 7 4 years ago θ in QII cosθ = −2/3 sinθ > 0 > sinθ = √(1−cos²θ) = √(1−4/9) = √5/3 tanθ = sinθ/cosθ = −√5/2 θ in QIV sinθ = −2/3 cosθ > 0 cosθ = √(1−sin²θ) = √(1�If the terminal arm of an angle in standard position lies in quadrants 2, 3, or 4, there exists a related acute angle (β) AND a principal angle (θ) If the terminal arm of the principal angle lies in quadrant 2 then the related acute angle is calculated as β = 180° θ If the terminal arm of the principal angle lies in quadrant 3 then the related acute angle is calculated as β = θIf given one trigonometric function, its value, and its quadrant, you can find the exact value of every double angle identity For example, if told to find the exact value of sin2u given $\text{sec(u)}=\frac{9}{2}$, for $0\leq\text{u}\leq\frac{\pi}{2}$ (u is in quadrant 1) You may begin solving the problem by examining the equation for sin2u According to the formula for sin2u, the
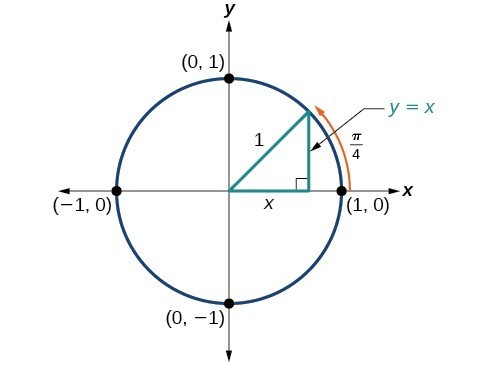


Unit Circle Sine And Cosine Functions Precalculus Ii
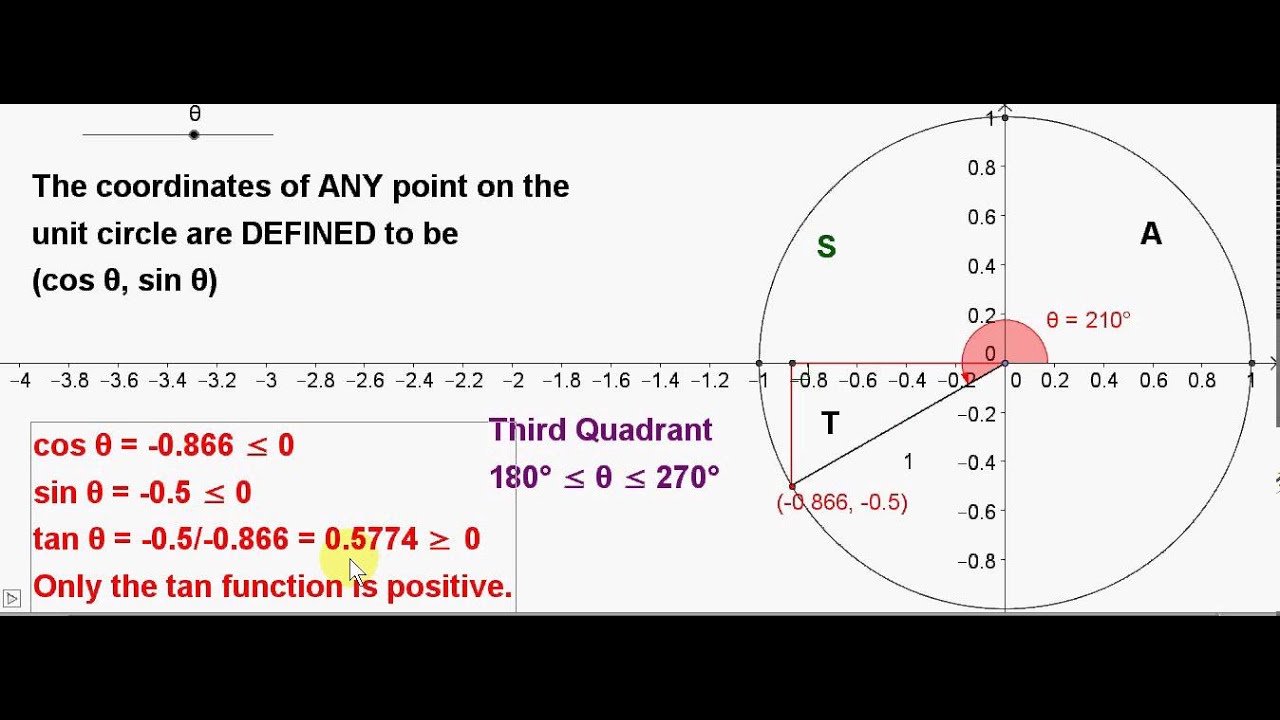


Unit Circle Angles In The Third Quadrant Youtube
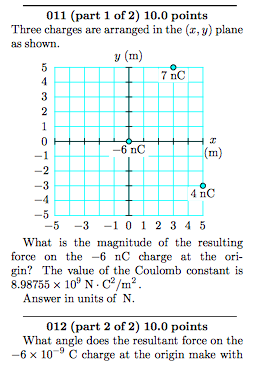


Solved Part 2 What Angle Does The Resultant Force On Th Chegg Com



Reference Angle Calculator Definition Graph Quadrants


Special Angles In The Unit Circle
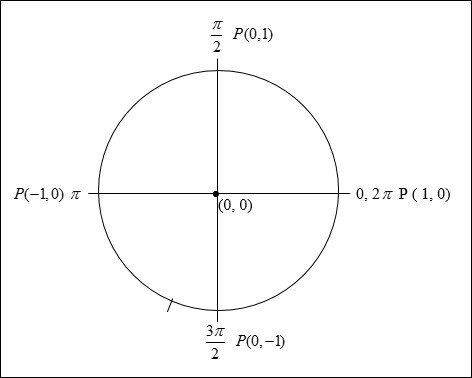


Circular Trigonometry
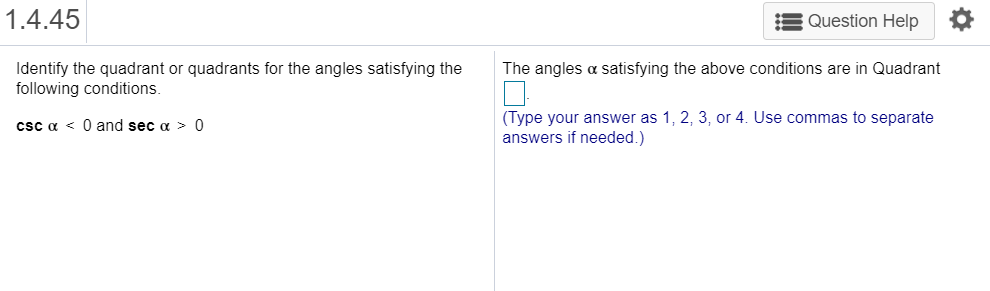


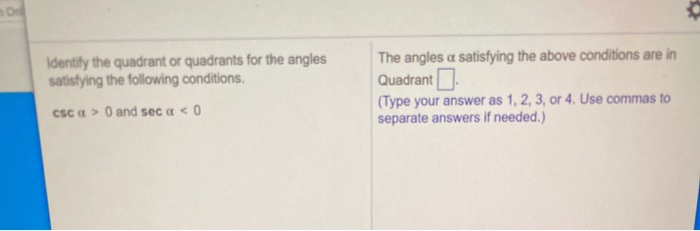
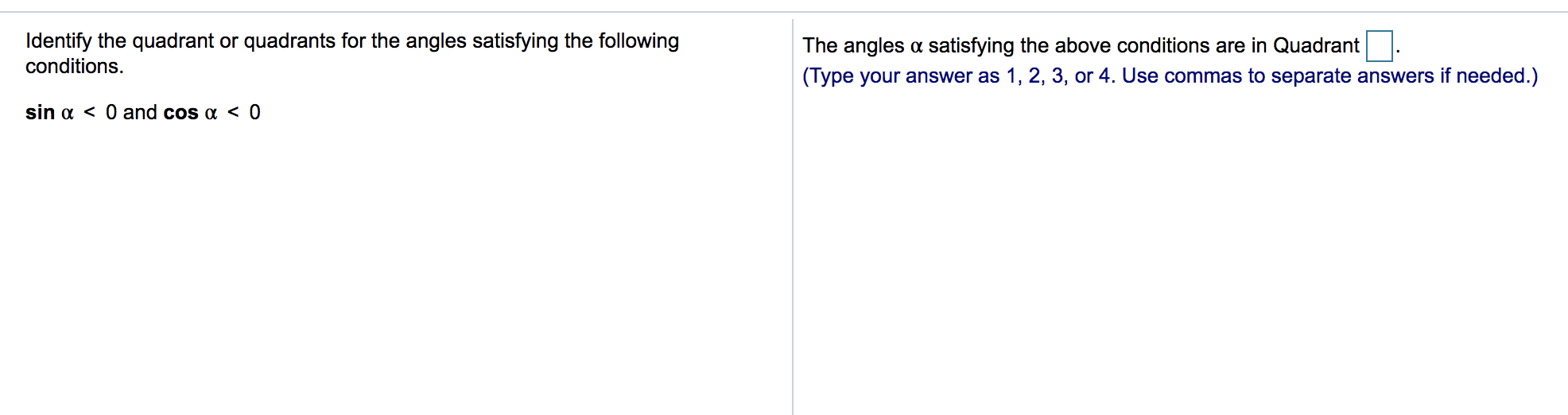
Solved 1 4 45 Question Help The Angles A Satisfying The A Chegg Com


Quadrant Plane Geometry Wikipedia
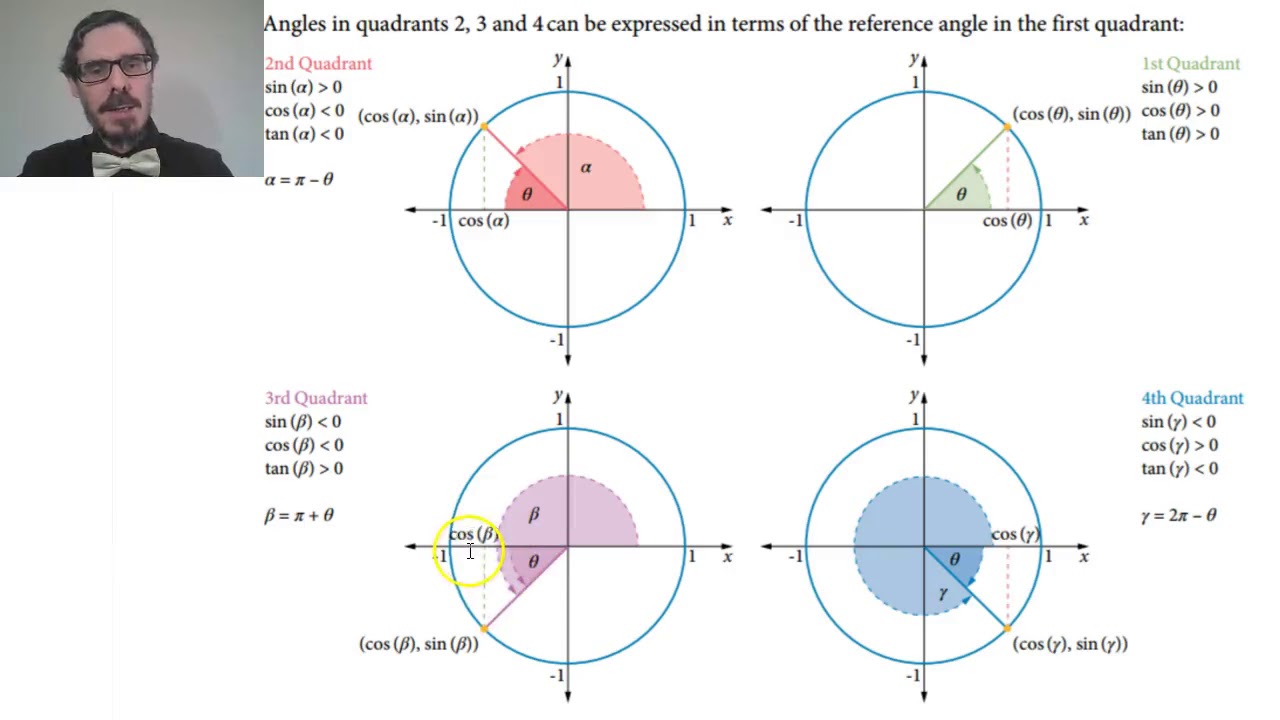


7 1a Reference Angles And 4 Quadrants Youtube
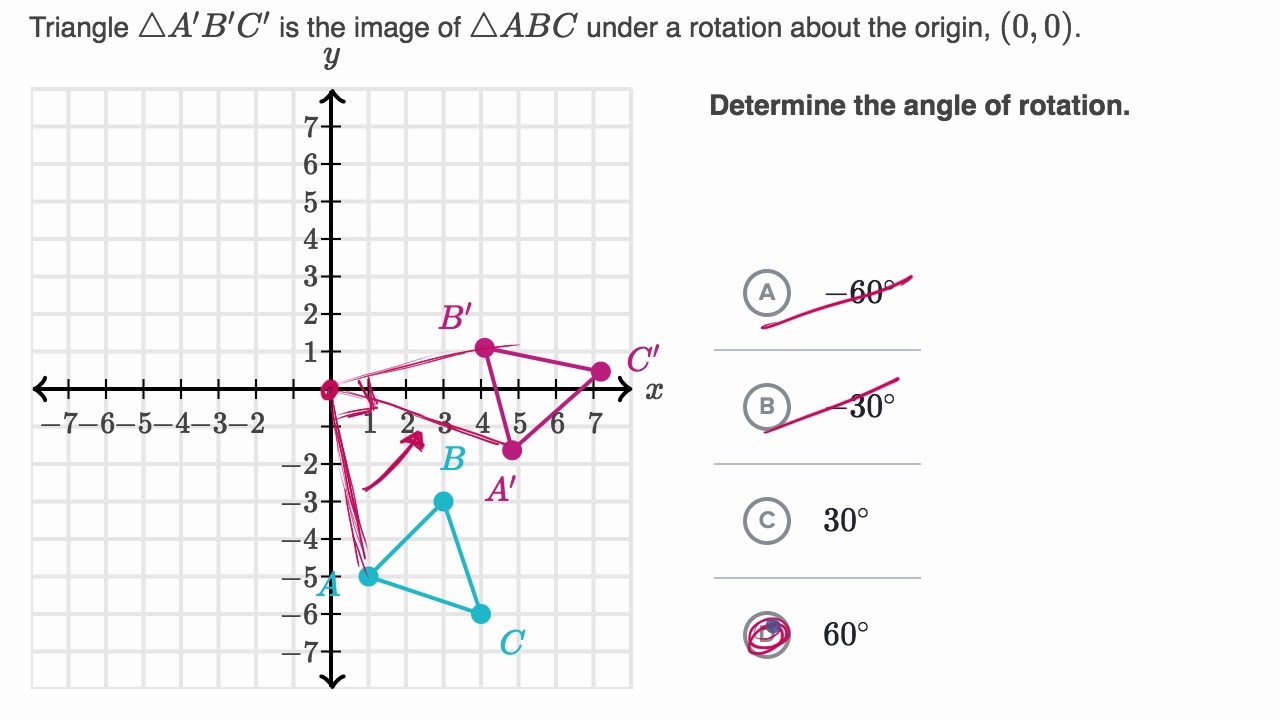


Determining Rotations Video Rotations Khan Academy
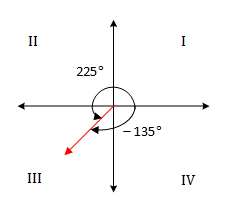


Trigonometry Quadrants And Quadrantal Angles


Coordinates And Graphs Of Lines
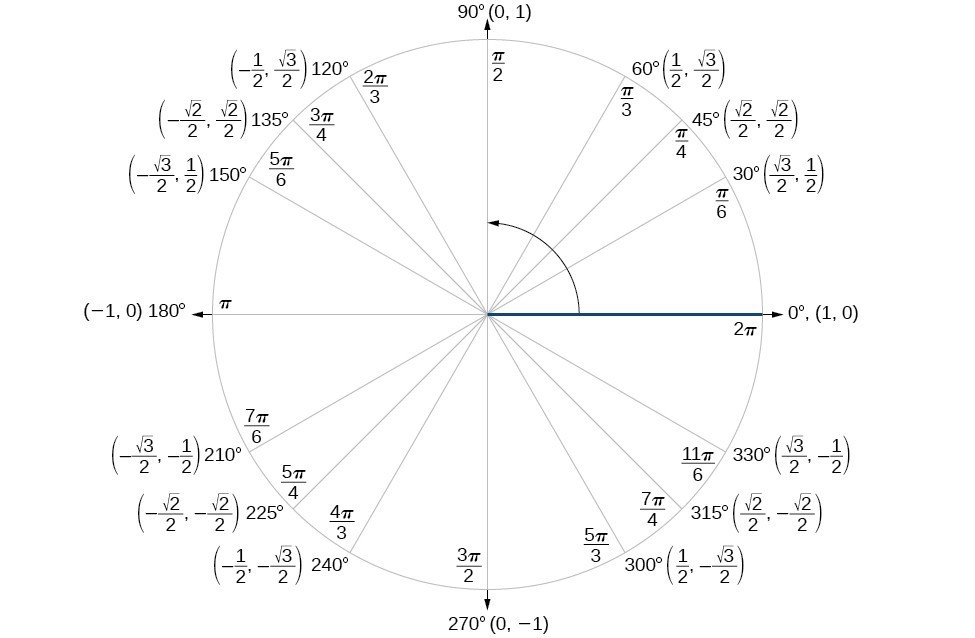


Sum And Difference Identities Precalculus Ii



Content The Four Quadrants



Chapter 4 Title Page 4 Lesson 3 Primary Trig Ratios Special Angles 2 A To Find



6 1 Angles In Standard Position In Quadrant I Youtube



10 1 Angles And Their Measure Mathematics Libretexts
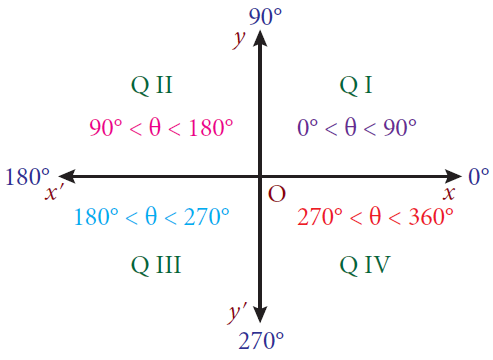


How To Determine In Which Quadrant An Angle Lies



Solved 1 The Right Triangle Below Is Inscribed I Central Chegg Com


Trigonometric Functions Of A General Angle


In What Quadrant Does The Angle 0 Degrees Lie Quora



Rectangular Coordinate System


Exact Trig Values



Pdf Half Angles Sequence Of Pi Integral Formulas


Year 10a Chapter 04 Introducing The Unit Circle Activity Builder By Desmos


The Coordinate Plane
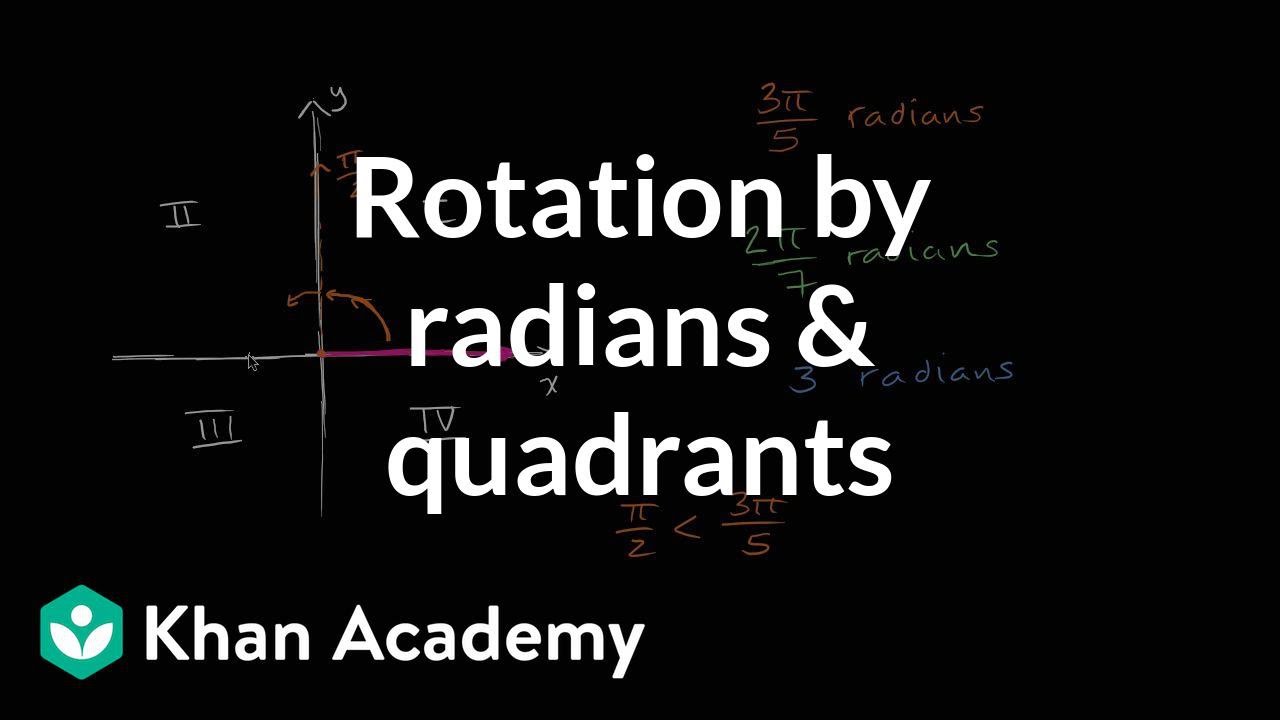


Radian Angles Quadrants Video Radians Khan Academy



Trig Angles And Rotation



Trigonometric Constants Expressed In Real Radicals Wikipedia



1 4 Trigonometric Functions Of Any Angle Mathematics Libretexts


How Do You Find The Related Acute Angle Example


Unit Circle Trigonometry


Find Reference Angle



The Unit Circle Ck 12 Foundation



Unit Circle Angles In The Second Quadrant Youtube


Solved 5 Points My No Graph The Oriented Angle In Stand Chegg Com


Solved Identify The Quadrant Or Quadrants For The Angles Chegg Com



Reference Angle Calculator Definition Graph Quadrants


Quadrants



Reference And Coterminal Angles These Are Two Or



The Unit Circle First Quadrant Angles



Solved 1 2 Give An Expression That Generates All Angles Chegg Com



Content The Four Quadrants
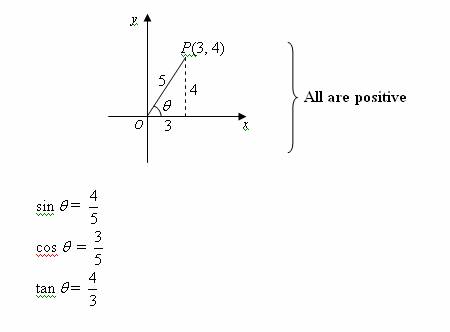


Trigonometric Ratios Solutions Examples Videos
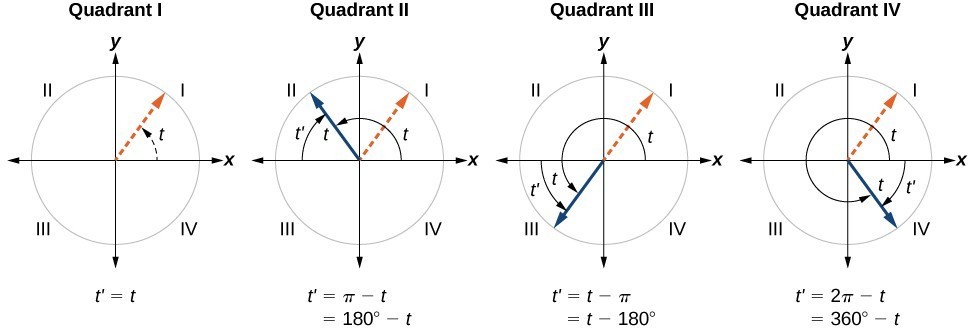


Section 4 4 Reference Angles Precalculus
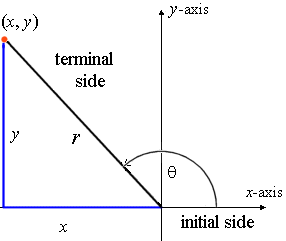


5 Signs Of The Trigonometric Functions



Which Triangle Defined By Three Points On The Coordinate Plane Is Congruent With The Triangle Brainly Com



Exercise 12 4 Page 352 Assignment 2 Solutions Exercise 12 30 40j 30 40 40 30 40 50 Tan Tan 53 306 30 50 306 50 Cos306 Jsin306 To Graph Plot Point 30 40 In 4th Studocu



Sine Cosine And Tangent In Four Quadrants
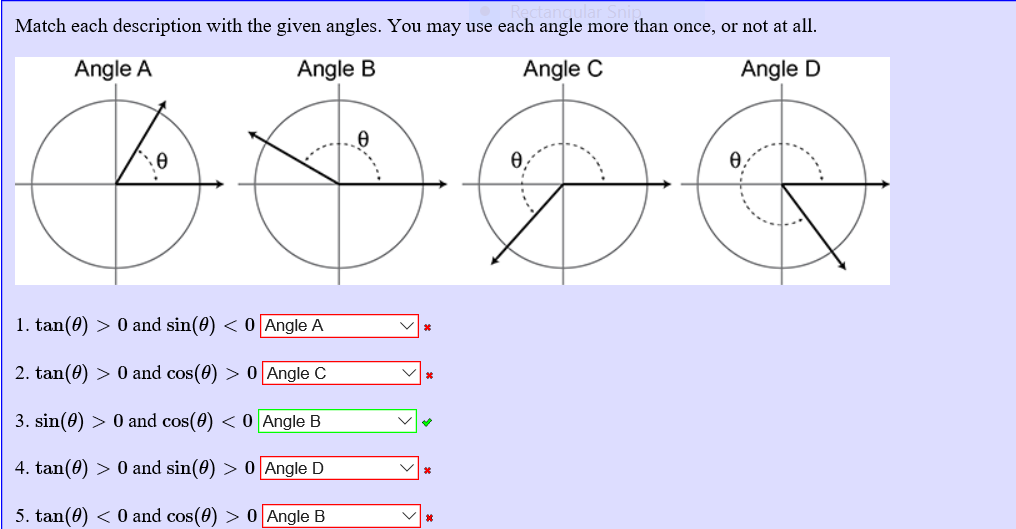


Solved Match Each Description With The Given Angles You Chegg Com



Rectangular Coordinate System



3 Ways To Memorize The Unit Circle Wikihow
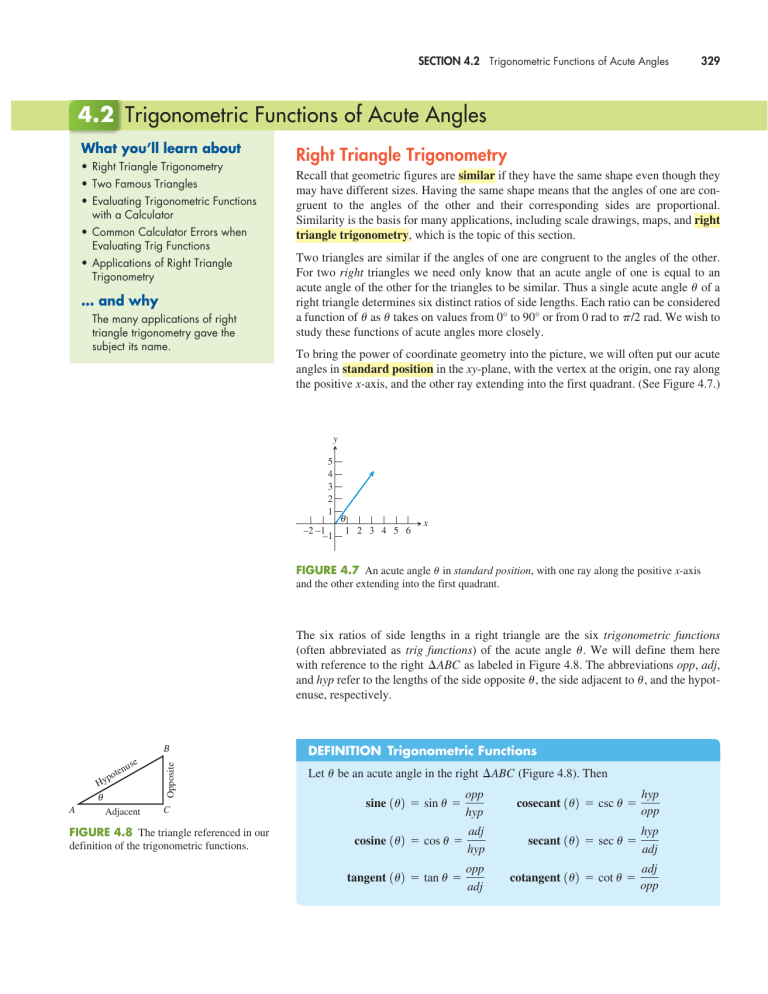


4 2 Trigonometric Functions Of Acute Angles Manualzz



Rectangular Coordinate System


Unit Circle Trigonometry


Trigonometry Quadrants And Quadrantal Angles



3rd Quadrant On Unit Circle Page 2 Line 17qq Com


What Comes Next Here Is A Sequence Of Letters Ppt Video Online Download



Activity 4 2 Trig Ratios Of Any Angles


Trigonometry Quadrants And Quadrantal Angles



Sine Cosine And Tangent In Four Quadrants
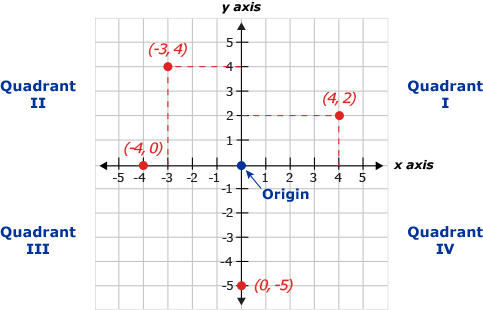


I Pathways Learning Pathways In Adult Education



Coordinate Plane Worksheets 4 Quadrants


Cast Rule Mathonline



Answered Use Reference Triangles In An Bartleby
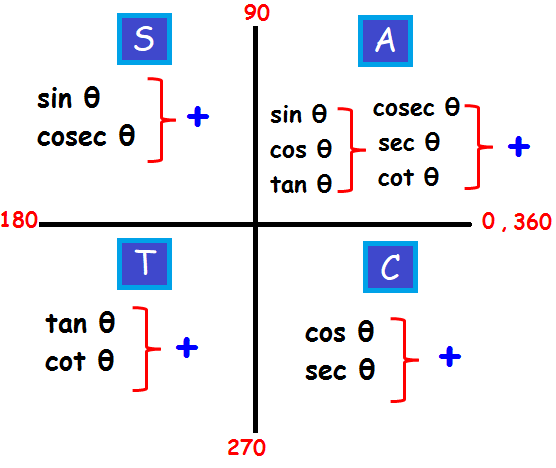


Trigonometry Quadrant Formulas



Content Radian Measure


If Tan 8 Is Positive And Sin 8 Is Negative In Which Quadrant Does 8 Lie Quora
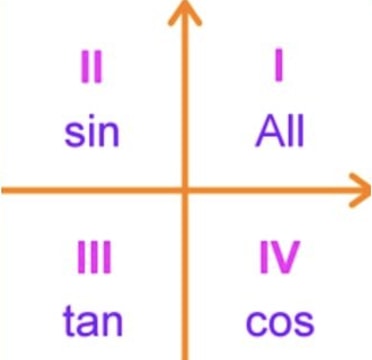


What Is All Students Take Calculus In Trig Studypug
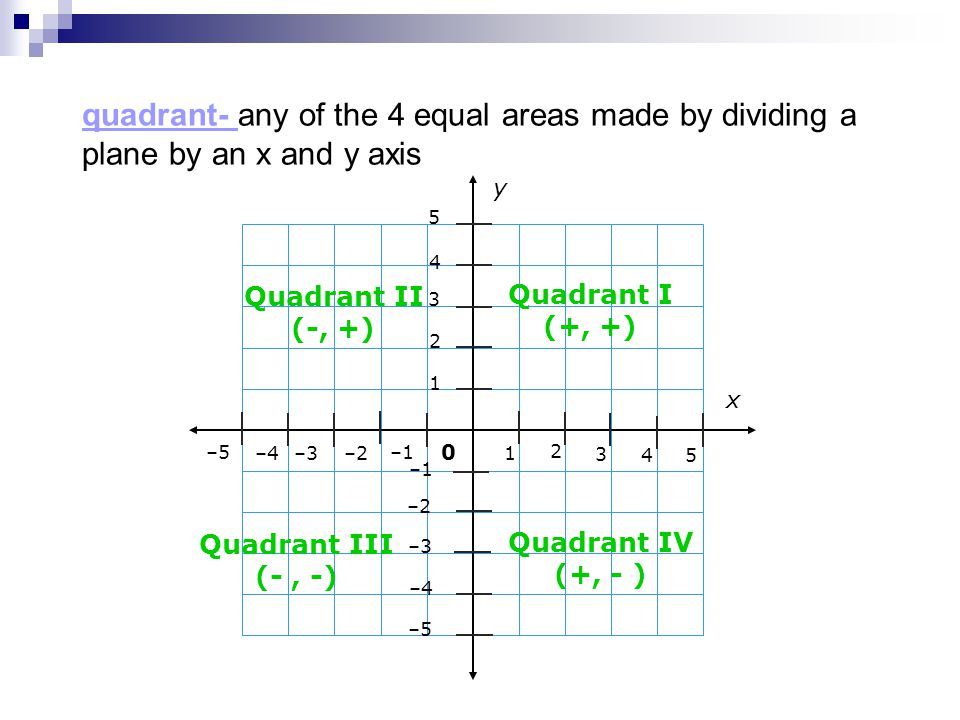


Graph Each Integer And Its Opposite On A Number Line Ppt Download



1 5 Plotting Points On A Coordinate Grid Gruending Math 6



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿